React: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
ReactJS is a powerful and widely-used JavaScript library for building dynamic and interactive user interfaces, especially for single-page applications (SPAs). Developed by Facebook, React allows developers to create reusable UI components that efficiently update and render based on data changes.
One of React’s key features is the Virtual DOM, which improves performance by updating only the necessary parts of the real DOM. React uses a component-based architecture, where applications are built by composing small, independent components that manage their own state and behavior. These components can be functional (simpler, using hooks like useState and useEffect) or class-based (which use lifecycle methods like componentDidMount).
React also introduces JSX (JavaScript XML), a syntax extension that allows developers to write HTML-like code within JavaScript, making UI development more intuitive. State management in React helps in handling dynamic data, and props allow components to communicate with each other by passing data.
React’s declarative approach to UI development makes it easier to design predictable and maintainable applications. Additionally, it integrates seamlessly with tools like Redux for state management, React Router for navigation, and testing libraries like Jest. With a vast ecosystem and community support, React remains a top choice for front-end web development.
Is React Back-End or Front-End?
React is a front-end JavaScript library designed for building user interfaces, primarily for web applications. It focuses on rendering components and managing the view layer, enabling developers to create dynamic and interactive user experiences.
Although React itself does not handle back-end operations like database management or server-side logic, it can seamlessly interact with back-end services through REST APIs or GraphQL. This makes it a crucial part of full-stack development when paired with back-end technologies such as Node.js, Express, Django, or Spring Boot.
In summary, React is strictly a front-end technology, responsible for building the UI, handling state, and improving performance with features like the Virtual DOM. However, it can work alongside back-end frameworks to create full-fledged web applications.
Prerequisites for Learning React
Before diving into React, it is essential to have a strong foundation in the following technologies:
1. HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
HTML is the backbone of any web page. It provides the structure of a website by defining elements such as headings, paragraphs, images, buttons, forms, and more.
Key Concepts of HTML
- HTML Elements & Tags:
<div>,<p>,<h1> - <h6>,<img>,<a>,<button>, etc. - Forms & Inputs:
<input>,<textarea>,<select>,<form>(used for collecting user input). - Semantic HTML: Tags like
<article>,<section>,<nav>, and<footer>improve accessibility and SEO. - Attributes:
id,class,href,src,alt, etc., modify how elements behave.
Since React uses JSX (JavaScript XML), which looks similar to HTML, having a solid understanding of HTML will make working with React easier.
2. CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)
CSS is used to style and layout web pages. It controls the appearance of HTML elements, making web applications visually appealing and responsive.
Key Concepts of CSS
- Selectors:
class,id,tag,pseudo-selectors(e.g.,:hover,:nth-child()). - Box Model:
margin,border,padding, andwidth/heightaffect element spacing. - Flexbox & Grid: Used for layout design and alignment.
- CSS Preprocessors: SCSS/SASS for enhanced styling capabilities.
- Responsive Design: Media queries (
@media) help in designing for different screen sizes.
React often uses CSS Modules, Styled Components, or frameworks like Bootstrap and Tailwind CSS for styling.
3. JavaScript (JS) – The Most Important Prerequisite
JavaScript is the programming language that makes web pages interactive. Since React is built using JavaScript, mastering it is crucial before learning React.
Key JavaScript Concepts for React
1. Variables and Data Types
JavaScript supports different types of variables:
var(older, less commonly used)let(block-scoped, mutable)const(block-scoped, immutable)
Data Types in JavaScript:
- Primitive Types:
Number,String,Boolean,Null,Undefined,Symbol,BigInt. - Reference Types:
Object,Array,Function.
2. Functions and Scope
Functions allow code reuse and structure. JavaScript has multiple types of functions:
- Function Declarations:
- Function Expressions:
- Arrow Functions (ES6+):
- Scope in JavaScript:
- Global Scope: Accessible anywhere in the script.
- Local Scope: Accessible only inside a function or block.
- Block Scope: Limited to
{}blocks (applies toletandconst).
3. Arrays and Objects
- Arrays store multiple values in a single variable:
- Objects store key-value pairs:
- Array Methods:
.map()– Loops through an array and returns a new array..filter()– Filters elements based on a condition..reduce()– Accumulates values in an array.
4. Loops and Iteration
JavaScript loops help iterate over arrays and objects.
- For Loop
- While Loop
- Array Iteration (
map)
5. DOM Manipulation
React replaces direct DOM manipulation with Virtual DOM, but it’s essential to understand basic DOM methods.
document.getElementById("myElement").innerText = "Hello!";
querySelector(), createElement(), appendChild() are also frequently used.
6. Promises and Asynchronous Programming
JavaScript handles asynchronous operations using Promises and async/await.
- Promise Example:
- Async/Await Example:
7. ES6+ Features (Essential for React)
- Destructuring
- Spread and Rest Operators
- Template Literals
- Modules (import/export)
- Optional Chaining (
?.)
Key Concepts of React
React is built on several fundamental concepts that make it efficient, scalable, and easy to use. These include components, JSX, the virtual DOM, state, and props. Let’s explore each in detail.
1. Components in React
Components are the building blocks of a React application. A React app is made up of multiple components that work together to create a seamless user interface. Each component is independent and reusable, making the development process efficient and maintainable.
There are two main types of components in React:
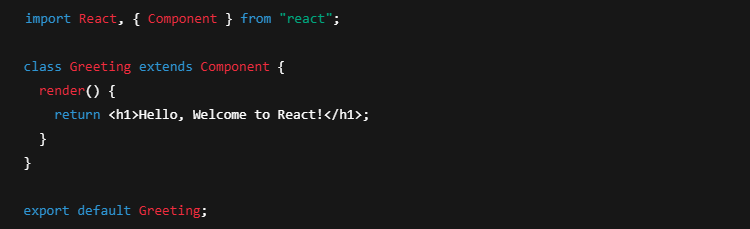
(a) Functional Components
Functional components are JavaScript functions that return JSX. They are the simplest way to create components and are often used for presentational purposes.
Example of a Functional Component:

Key Features of Functional Components:
✔ Simple and easy to understand.
✔ Use React Hooks (like useState and useEffect) for state and lifecycle management.
✔ Preferred over class components in modern React development.
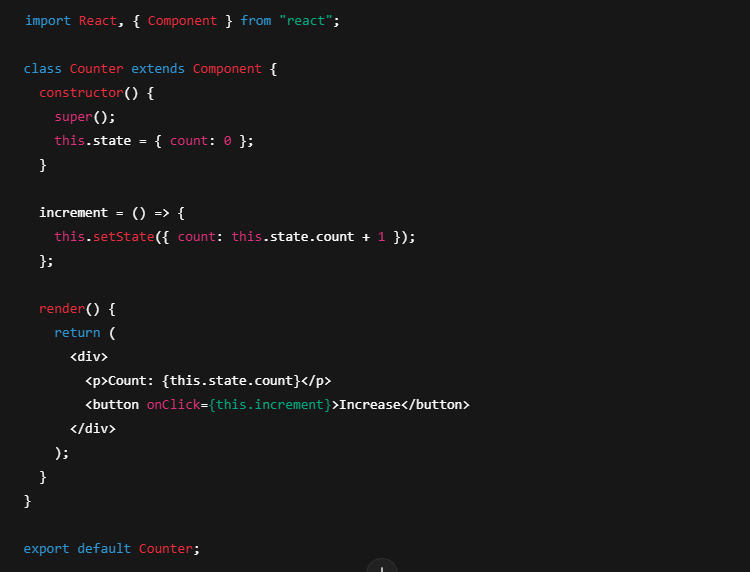
(b) Class Components
Class components are ES6 classes that extend React.Component. They were used before React Hooks were introduced and include lifecycle methods.
Example of a Class Component:
Key Features of Class Components:
✔ Use this.state for state management.
✔ Contain lifecycle methods (componentDidMount, componentDidUpdate, etc.).
✔ More verbose than functional components.
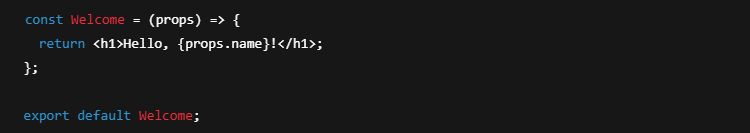
(c) Props (Properties)
Props allow components to receive data from a parent component and render dynamically. Props are read-only and cannot be modified inside the child component.
Example of Props:
Using the Component with Props:
Key Features of Props:
✔ Passed from parent to child components.
✔ Immutable (cannot be changed inside the child component).
✔ Help in making components reusable.
(d) State
State is a built-in object in React that allows components to store and manage dynamic data. Unlike props, state is mutable and can change over time.
Example of State in Functional Components (using Hooks):
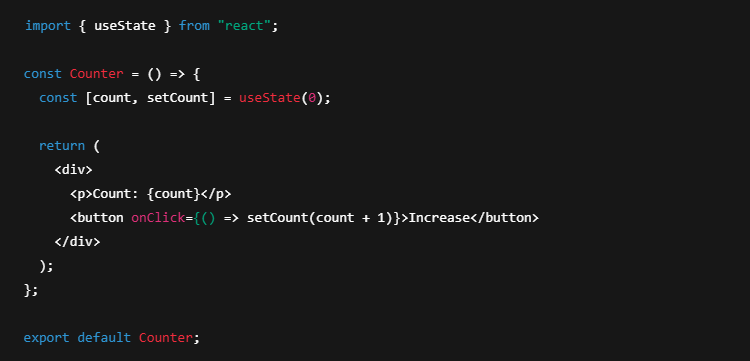
Example of State in Class Components:
Key Features of State:
✔ Mutable (can be changed within the component).
✔ Used for managing data that affects rendering.
✔ Changes trigger a re-render of the component.
2. JSX (JavaScript XML)
JSX is a syntax extension that allows us to write HTML-like code inside JavaScript. JSX makes the code more readable and expressive.
Key Features of JSX:
✔ Looks similar to HTML but is compiled into JavaScript.
✔ Makes UI code easier to understand.
✔ Allows embedding JavaScript expressions using {}.
✔ JSX must return a single parent element (use <div> or <> fragments if needed).
3. Virtual DOM
The Virtual DOM is a lightweight copy of the real DOM that React uses to improve performance.
How Virtual DOM Works:
- When state or props change, React updates the Virtual DOM instead of modifying the real DOM directly.
- React compares the updated Virtual DOM with the previous one (using “diffing”).
- It then updates only the changed parts in the real DOM instead of re-rendering the entire page.
Key Benefits of Virtual DOM:
✔ Improves performance by reducing direct DOM manipulations.
✔ Efficient updates through reconciliation.
✔ Enhances user experience by making UI updates faster.
4. State in React
State is one of the most crucial concepts in React, as it allows components to have dynamic behavior.
Key Features of State:
✔ Local to the component (not accessible from outside unless passed as props).
✔ Triggers re-renders when updated.
✔ Managed using useState in functional components and this.state in class components.
✔ State should never be modified directly (always use setState or equivalent).
5. Props in React
Props (short for properties) are used to pass data from one component to another.
Props vs. State
| Feature | Props | State |
|---|---|---|
| Mutability | Immutable | Mutable |
| Ownership | Passed from parent | Managed within component |
| Scope | Available in child components | Local to the component |
| Updates | Does not trigger re-render | Triggers re-render |
Recent On cloudxtech
Mastering GitHub from the Command Line: Push, Pull, and Repo Management Made Easy
September 4, 2025 • 5 minute(s) read
10 Fun HTML, CSS, and JavaScript Projects to Practice and Improve Your Skills
August 26, 2025 • 11 minute(s) read
Beginner Frontend Projects with HTML, CSS, JS, and jQuery – Free to Use and Download
August 11, 2025 • 4 minute(s) read
Best Chrome Extensions for Web Developers in 2025
June 12, 2025 • 3 minute(s) read
JN Form Validation: Simplify Client-Side Validation with Ease
May 22, 2025 • 4 minute(s) read
🌊 The Indus Waters Treaty: A Historic Pact and its Dramatic Suspension in 2025
April 27, 2025 • 5 minute(s) read